United Precision Plastics
(Manufacturers of Packaging Solutions)
Reassuring Quality

Compostability
The term “bioplastics” is actually used for two separate things:
Bio-based plastics :
-
This means that the material is (partly) derived from biomass or plants ie which are renewable sources.
-
Biomass for plastics are usually from corn, sugarcane, or cellulose. Therefore this is not fossil fuel based, hence it is also called as Green material
Biodegradable plastics :
-
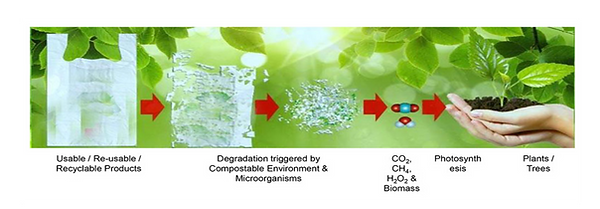
Plastics that can be completely broken down by microbes in a reasonable timeframe, given specific conditions.
-
Micro-organisms in the environment are able to convert biodegradable materials to natural substances such as water, CO2, and compost without additives within a certain time and at a particular location.
NOTE: Not all bio-based plastics are biodegradable, and not all biodegradable plastics are bio-based.
Bio-based plastics : “Beginning of Life” of plastics
Biodegradable/compostable: “End of life of plastics

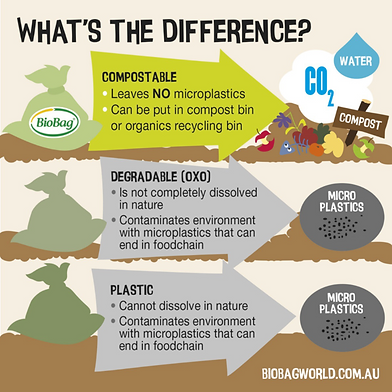
What does compostability mean ?
Fragmentation – first step in the biodegradation process, in which organic matter is broken down into microscopic fragments
Biodegradability – Complete microbial assimilation of the fragmented product as a food source by the microorganisms in the disposal environment
Compostability – Complete carbon assimilation within 180 days in an industrial compost environment.
.png)
Bio-based And Bio Degradable: These are usually materials
made from cellulose acetate (plant-based) or lactic acid-based
blends (or pure starch blends) and are used for primarily single
use plastics like cutlery or some applications across pens/toys etc.
Some examples are :
PLA : Poly Lactic Acid
PHA : Poly Hydroxyalkanoate
And other plant based cellulose compounds
They are completely biodegradable as per the standards specified
under ASTMD6400 / EN13432
Oil-Based and Bio-degradable : Traditional oil based polymers
which are biodegradable have existed for many years and usually
being used for applications such as stents, tissue engineering
and other biomaterial applications.
Some examples are :
uPBAT, PBS and PCL
.png)
CIPET: BIODEGRADABILITY TEST REQUIREMENTS
-
Biodegradation/Mineralization:
Ultimate aerobic Biodegradation ( the breakdown of organic contaminants such as carbon by microorganisms when oxygen is present) must be more than 90% within 180 days
-
Disintegration:
After 12 weeks not more than 10% of the product’s original dry mass should remain when passing through 2mm sieve
-
Ability of compost to support plant growth:
The Percentage of Seed germination should be greater than 90% for 2 different plant species.